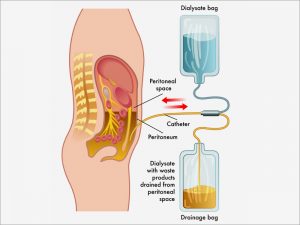
Peritoneal dialysis is a very simple technique that is performed daily at the patient’s home, there are two types: Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) or manual and Automatic Peritoneal Dialysis (APD) with machine or cycler.
What is peritoneal dialysis?
It is dialysis performed daily by the patient at home after a period of learning. It only requires a sufficient space to store the material and a suitable and well-ventilated place to perform the technique, which can be the room itself.
It is recommended that there be no animals at home.
Access peritoneal dialysis:
The peritoneal fluid is introduced into the peritoneal cavity through a soft silicone catheter or tube, which is placed through a small surgical incision in the abdomen at least one month before use.
This catheter is hidden under clothing and does not interfere with any type of activity. It only requires some simple cleaning care that is learned in the training phase.
The training:
It begins when a month after the placement of the catheter. It is performed in the Peritoneal Dialysis Unit by the nurse responsible for their training. It consists of learning a few simple steps perfectly ordered so that during the change of dialysis fluid you maintain at all times the cleaning measures necessary to avoid infections.
It is not necessary to have any health knowledge and it can be done at any age. The duration of the training will be adapted to your needs.
Types of peritoneal dialysis:
There are two types of peritoneal dialysis:
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) or Manual.
- Automatic Peritoneal Dialysis (DPA), with machine or cycler.
- In the CAPD (manual) peritoneal fluid changes are made 3-4 times a day. The schedule of exchanges is approximate, depending on the routine and unforeseen that may arise, recommending that at least the permanence of the liquid is a minimum of 4 hours and a maximum of 8 hours.
- In the DPA (cycler) the periodic changes are made by a machine called a cycler during the night while you are sleeping. The last fluid change is the one that remains throughout the day in the abdomen until night when the cycler empties the abdomen just connect.
Regardless of whether you dialyze with a cycler, you must first perform manual dialysis training in order to continue dialysis in case of machine failure, power outages or weekend trips, etc.
The DPA (cycler) is especially indicated when you want to maintain work activity without interference.
Advantages and disadvantages of peritoneal dialysis:
Advantage:
- It is a continuous treatment that is done throughout the day, mimicking your own kidneys, not leading to accumulation of toxins or water in the body.
- It is done at home and only goes to the hospital for tests and reviews (more or less every 3 months).
- As it is done by a catheter located in the abdomen, it is not necessary to puncture the veins repeatedly.
- It is a simple technique applicable at any age, which allows a flexible schedule, which gives autonomy and allows you to reconcile your work and social life.
Disadvantages:
- You are the one who performs the treatment, except in exceptional cases, and therefore requires active involvement in it.
- The presence of the catheter in the abdomen, which on the other hand does not interfere with any activity, may be uncomfortable or unsightly.
- At home, you need an adequate and conditioned space to carry out the treatment and store the material.
Storage of material:
The material is received once a month for what is needed:
- A sufficient and conditioned space.
- Avoid extreme temperatures and away from humidity
- It must be kept in closed boxes to avoid breakage or deterioration.
- Sort bags according to your glucose concentration, it facilitates control of stocks, expiration and helps you avoid mistakes.
You can make short trips (less than 7 days) carrying your own material. If the duration is longer, your usual provider will provide your treatment at your vacation place.